Do you know what keeps the Earth in its orbit while going around the Sun? It’s gravitational potential energy. Further, when you see a roller coaster on the ground, it has kinetic energy transformed into gravitation potential energy. But do you know how these energies are different and how interconversions happen? Let’s compare kinetic energy vs potential energy.
This comparison will surely take you back to the potential vs kinetic energy worksheet in school. Here’s a chance to hone your knowledge.
Contents
Kinetic Energy Vs Potential Energy Differences

Kinetic is a derivative of the Greek word kinesis, meaning motion. The recent form or concept of kinetic energy has developed in the 19th century. William Thomson, or Lord Kelvin, coined this term around 1850.
On the other hand, Scottish Physicist William Rankine came up with the term potential energy.
Here is an easy-to-comprehend kinetic energy vs potential energy comparison spread across seven parameters.
1. Kinetic Energy Vs Potential Energy Definition
Cambridge Dictionary defines kinetic energy as an “energy that an object or system has because it is moving.”
Let me explain. Kinetic energy refers to the energy of a body or system with respect to the particles’ (in a system) or body’s motion.
Further, the Cambridge Dictionary defines potential as “the energy stored by something because of its position (as when an object is raised), because of its condition (as when something is pulled or pushed out of shape), or in chemical form (as in fuel or an electric battery).”
To put it simply, an object has a certain position or configuration. Thanks to the configuration or position, some energy is stored in the object, and that is called potential energy.
2. Potential Vs Kinetic Energy Formula

You will get the formula of the potential energy based on the force that acts on two objects. The formula for the gravitational force is W = m×g×h = mgh.
- M refers to mass in kilograms.
- G refers to acceleration caused by gravity.
- H refers to height in meters.
The unit of potential energy is kg m2 / s2. Joule (J) unit is used to measure this energy.
The formula for kinetic energy is KE = ½ mv2
M refers to the mass of the object, and V refers to its velocity.
The unit of kinetic energy is kg m2 / s2. Joule (J) unit is used to measure this energy.
3. Kinetic And Potential Energy Connection To The Environment

Other moving and stationary objects in the immediate environment can impact the kinetic energy of an object.
However, potential energy does not get impacted by other mobile or stationary objects in the immediate environment.
4. Potential Energy Vs Kinetic Energy Transferability
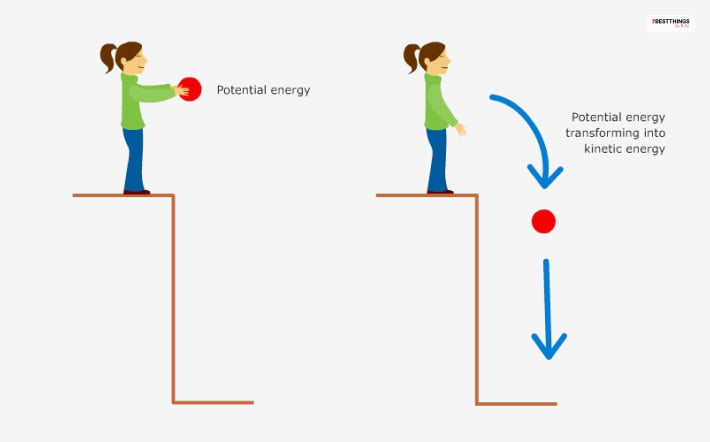
An object cannot transfer its potential energy to another. The potential energy one object has is solely based on its position and configuration, and that cannot be changed.
However, kinetic energy is transferable. When two objects come in, they come in contact or collide.
5. Examples Of Kinetic Energy And Potential Energy
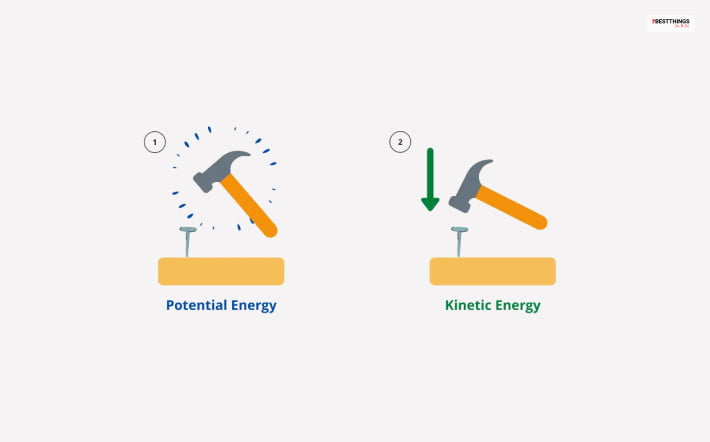
You will find some easy examples of kinetic and potential energy in nature. When water flows from a waterfall, it is an example of kinetic energy.
However, when the same water is stored in a small pond or swimming pool, the water has potential energy.
6. Kinetic Energy Vs Potential Energy: Different Types

Kinetic energy is of two types: rotational kinetic energy and translational kinetic energy.
Potential energy can be of multiple types. These are:
- Nuclear potential energy
- Gravitational potential energy
- Electrical potential energy
- Chemical potential energy
- Elastic potential energy
The classification of potential energy happens because of the change in the “applicable restoring force.”
7. Potential And Kinetic Energy Determining Factor
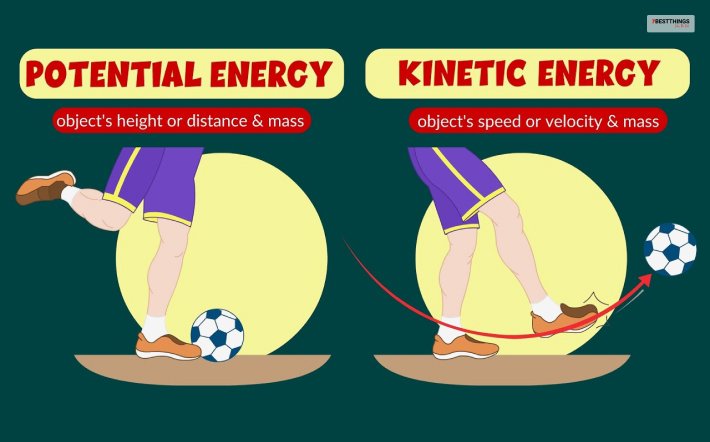
The determining factors of potential energy are “height or distance and mass.”
However, the determining factors of kinetic energy are “speed or velocity and mass.”
Interconversion Of Kinetic Energy And Potential Energy
The law of conservation of energy says that you cannot destroy any energy. Energy can be transformed from one form to another.
For example, when a pendulum moves, it keeps going upward and reaches the highest point according to its highest potential energy.
However, when the pendulum moves downward, the potential energy gets converted into kinetic energy.
Thus, the interconversion happens.
Further, a metal spring has a certain potential energy, and that helps enable you to stretch the spring. Now, when you stretch the spring, it puts pressure on the opposite side so that it can come back to its actual position.
When you release the other part of the spring, and it comes back to its actual position, the potential energy gets converted into kinetic energy.
Also, remember that potential energy will always be higher than kinetic energy. The simple reason is that when potential energy gets converted into kinetic energy, some loss of energy occurs. To explain further, when the conversion happens, some amount of potential energy gets transformed into light energy and heat energy. Even friction results in some energy loss.
Final Words
Summing up the kinetic energy vs potential energy comparison, I can say that potential energy is the energy of an object when it’s static. The energy comes from its position or configuration.
However, when the same object starts movements or has motion, the potential energy gets converted to kinetic energy.
Many examples in nature show the interconversions of potential and kinetic energy.
Potential energy, in its pristine form, cannot affect or impact the environment. It only impacts the immediate environment or other objects in the environment when it gets transformed into kinetic or any other type of energy.
The potential object of a heavy object placed at a higher altitude will always be greater than a light object placed at a lower height.
An object has the highest potential energy when it is in its solid state. The potential energy goes down as per its changing state. It goes like solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. So, the plasma state has the lowest potential energy and the highest kinetic energy.
Do you want to point out any other differences between these two energies? Don’t forget to share.
Also Read












